In today’s fast-paced, modern world, obesity and lifestyle diseases have become an ever-growing concern for individuals and society as a whole. These challenges and social well-being. It is crucial now, more than ever, to be proactive in addressing have far-reaching implications, not only for physical health but also for emotional. these issues and taking responsibility for our own health. This comprehensive guide, “Combating Obesity and Lifestyle Diseases: A Guide to Overcoming Through Preventive Healthcare Strategies,” serves as a beacon of hope and empowerment, providing readers with the tools and knowledge necessary to overcome these health challenges. We will explore the root causes of obesity and lifestyle diseases, delve into the importance of preventive healthcare, and present actionable strategies to help individuals lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Understanding the Prevalence and Causes of Obesity and Lifestyle Diseases
Obesity is a condition characterized by having an excessive amount of body fat. It is typically diagnosed based on a person’s body mass index (BMI), which is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 650 million adults worldwide were obese in 2016.
Lifestyle diseases are chronic conditions that are often preventable by making positive lifestyle changes. These conditions include type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. According to the American Diabetes Association, over 34 million Americans have diabetes, and it is estimated that over 70% of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese. Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, responsible for over 17 million deaths in 2019 alone.
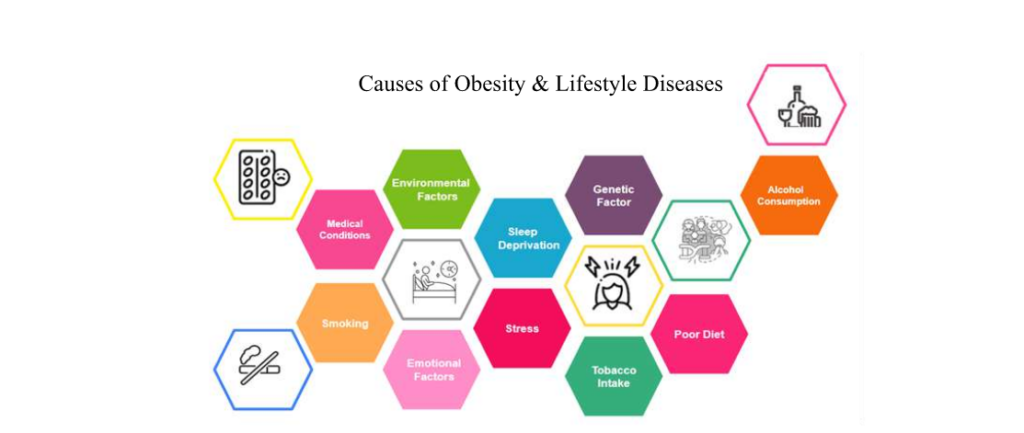
Obesity and lifestyle diseases are caused by a combination of factors, including genetic predisposition, unhealthy eating habits, lack of physical activity, and certain medical conditions. Unhealthy eating habits include consuming foods high in calories, fat, sugar, and salt, while not getting enough fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Another factor that contributes to obesity and lifestyle diseases is physical inactivity. People who are physically inactive are more likely to gain weight, which can lead to obesity. Let’s delve into the causes of obesity and lifestyle diseases in detail.
Genetic Factors:
Genetic predisposition plays a role in the development of obesity and lifestyle diseases. Certain genes can influence an individual’s metabolism, appetite, and fat storage, making them more susceptible to weight gain and associated health issues.
Poor Diet:
A diet high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, sugars, and low in essential nutrients, fiber, and whole foods can contribute to obesity and lifestyle diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
Sedentary Lifestyle:
Lack of physical activity and an increased reliance on technology and sedentary forms of entertainment can lead to weight gain and increased risk for lifestyle diseases. Regular exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of chronic conditions.
Stress:
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, increased appetite, and poor food choices, which can contribute to obesity and lifestyle diseases. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or mindfulness can help maintain a healthier lifestyle.
Sleep Deprivation:
Insufficient sleep can disrupt hormonal balance and increase appetite, leading to weight gain and increased risk for lifestyle diseases. Prioritising quality sleep is essential for overall health and well-being.
Socioeconomic Factors:
Economic status, education level, and access to healthy food options can influence an individual’s dietary choices and overall health. Addressing these socioeconomic disparities is crucial for reducing the prevalence of obesity and lifestyle diseases.
Environmental Factors:
The built environment, including the availability of safe spaces for exercise, walkability of neighbourhoods, and access to healthy food options, can impact an individual’s ability to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Creating supportive environments can help promote healthier behaviours.
Emotional Factors:
Emotional eating, using food as a coping mechanism for stress, anxiety, or depression, can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of lifestyle diseases. Addressing the emotional triggers and developing healthier coping strategies is essential for long-term weight management.
Medical Conditions and Medications:
Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Additionally, some medications can cause weight gain as a side effect. Consulting a healthcare professional to manage these conditions and explore alternative treatments when necessary can help mitigate their impact on weight and overall health.
Tobacco Intake, Smoking, and Alcohol Consumption:
Tobacco intake, smoking, and alcohol consumption are all risk factors for obesity and lifestyle diseases. These habits can lead to weight gain, decrease metabolism, increase appetite, and increase the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, liver disease, and diabetes. Reducing or eliminating these habits can help prevent and manage obesity and lifestyle diseases.
Overall, the rise of obesity and lifestyle diseases is a complex issue that is influenced by a variety of factors. Addressing these factors through preventive healthcare strategies, such as promoting healthy eating habits, increasing physical activity, and improving access to healthcare, can help prevent and manage these conditions and improve overall health outcomes
The Impact of Obesity and Lifestyle Diseases on Health and Well-being
The impact of obesity and lifestyle diseases on health and well-being is far-reaching, affecting various body systems and increasing the risk of developing other health issues. By understanding the consequences of these conditions, we can better appreciate the importance of preventive healthcare strategies and adopt healthier lifestyles.
Increased risk of chronic diseases:
These conditions can impair the cardiovascular system, leading to hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart failure. They also negatively affect the respiratory system, contributing to sleep apnea, asthma, and reduced lung function. In the endocrine system, obesity and lifestyle diseases can cause insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, damaging blood vessels and vital organs. Additionally, these conditions strain the musculoskeletal system, leading to osteoarthritis and fractures, and disrupt the digestive system, causing GERD, gallstones, and liver diseases.
Reduced quality of life:
Obesity and lifestyle diseases can impact an individual’s quality of life, causing physical limitations and reduced mobility. These conditions can also lead to social and emotional challenges, such as anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Increased healthcare costs:
The treatment and management of obesity and lifestyle diseases can be costly, both to the individual and to society as a whole. This can include expenses such as medication, medical procedures, and hospitalizations, as well as lost productivity and decreased economic output.
Impact on mental health:
Obesity and lifestyle diseases can also have an impact on an individual’s mental health. These conditions can cause feelings of shame, guilt, and low self-esteem, which can contribute to the development of mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Shortened life expectancy:
Obesity and lifestyle diseases are associated with a shortened life expectancy. These conditions increase the risk of premature death, particularly when they are not effectively managed or treated
Impact on the healthcare system:
The prevalence of obesity and lifestyle diseases places a significant burden on the healthcare system. This can include a strain on healthcare resources, increased demand for healthcare services, and a shortage of healthcare professionals.
The Importance of Preventive Healthcare in Combating Obesity and Lifestyle Diseases
As healthcare professionals, we have a unique opportunity and responsibility to promote preventive healthcare by adopting healthier lifestyles. Preventive healthcare is an important tool in combating obesity and lifestyle diseases, as it helps individuals to identify and address potential health risks before they manifest into severe conditions. Here are some strategies to implement:
Risk Factor Identification:
The first step is to identify the risk factors contributing to obesity and lifestyle diseases, such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, tobacco use, and excessive alcohol consumption. This helps to target specific areas where intervention is needed.
Risk Factor Modification:
By addressing modifiable risk factors, such as diet, physical activity, and smoking, preventive healthcare can help reduce the incidence of obesity and associated diseases. Healthcare professionals can educate patients on the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and provide them with the necessary tools and resources to make positive changes.
Early Detection and Intervention:
Implement appropriate screening measures for risk factors and early signs of lifestyle diseases, such as blood pressure monitoring, cholesterol testing, and diabetes screening. Regular screening for risk factors and early signs of lifestyle diseases enables timely intervention, preventing complications and reducing morbidity and mortality. Healthcare professionals can recommend appropriate screening tests and follow-up care for patients at risk.
Chronic Disease Management:
Preventive healthcare plays a crucial role in the management of chronic conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, by ensuring patients adhere to prescribed treatment plans and monitoring their progress. This helps reduce the risk of complications, improve the quality of life, and lower healthcare costs.
Preventive healthcare plays a pivotal role in combating obesity and lifestyle diseases by adopting a multifaceted approach that addresses risk factors, early detection, and management of these conditions.
Patient Education and Awareness:
Educate patients about the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and the risks associated with obesity and lifestyle diseases. Provide them with up-to-date information and resources to empower them to make informed decisions about their health.
Continuous Evaluation and Improvement:
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of preventive healthcare measures in combating obesity and lifestyle diseases. Use data-driven insights to improve existing strategies and implement new evidence-based practices to enhance patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the growing prevalence of obesity and lifestyle diseases presents a significant challenge to global health. However, by embracing and implementing preventive healthcare strategies, we can effectively combat these pressing issues. By focusing on healthy diets, regular physical activity, tobacco cessation, responsible alcohol consumption, stress management, and regular health screenings, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these chronic conditions. By adopting these strategies and fostering a culture of prevention and addressing the root causes of obesity and lifestyle diseases, we can work together to create a healthier society and ease the burden on our healthcare system. Ultimately, the key to overcoming and preventing these conditions lies in our collective commitment to prioritising preventive healthcare and making healthy choices a fundamental aspect of our daily lives.
Composed by: “Varsha, proficient as a Business Analyst, has an educational foundation in healthcare IT, acquired through a PGDHM from IIHMR Delhi. Her primary interest rests at the intersection of healthcare and technology, with a specific focus on harnessing cutting-edge tech solutions to revolutionize patient care and enhance healthcare systems. Her work areas comprise optimizing healthcare data flow and improving operational efficiency, driving enhanced patient care and system robustness.”

